In comparison to other dangerous workplaces, healthcare workers have a higher risk of injury and illness. Healthcare workers frequently lift and move their patients, causing injuries to the neck, back, shoulders, and other parts of the body. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), overexertion is a leading cause of approximately 45 percent of nonfatal occupational injuries and illnesses that result in people missing work. Musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) are the leading cause of missed workdays due to illness and injury in the healthcare industry.
What your employees need to know about handling patients safely
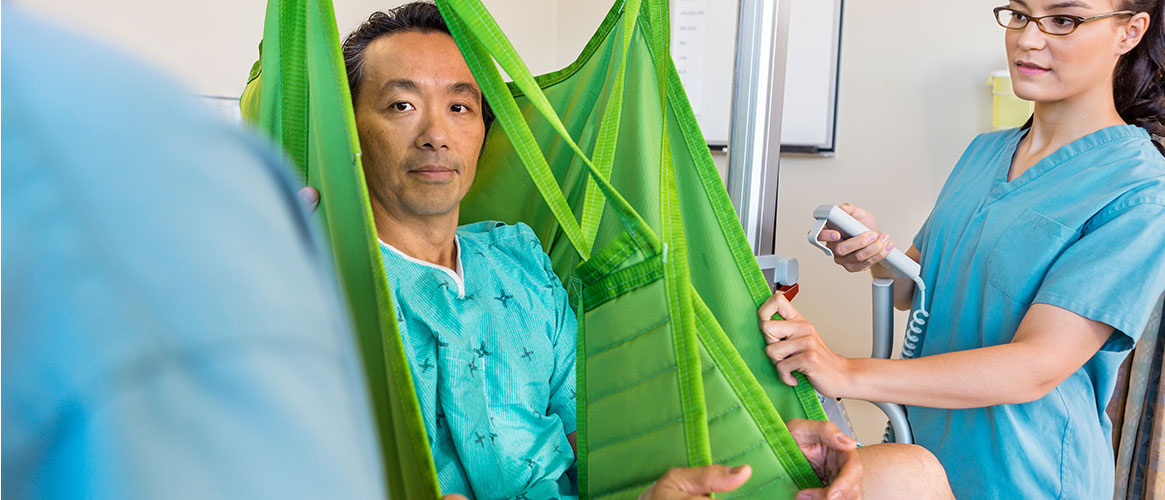
A mechanical lift is the safest way to move patients for both the healthcare worker and the patient. Mechanical lifts, specifically designed to eliminate any patient lifting, help by reducing the risk of back strains and other related injuries. However, if mechanical lifts are not available, lifting and moving a patient manually may be necessary.
Guiding patients into position, by bringing their hips forward, reduces the force required to lift the patient. The heaviest area of a person is located at about their waist (which is the center of mass). It is easier to get your patient out of a chair if you guide their head and shoulders forward as they bend their hips. In this way, the hips easily rise out of the chair, reducing the lifting force required.
Practice makes perfect. Learning the different handling techniques and understanding the reasons behind them allows your employees to figure out when to use the most appropriate techniques in different situations. Practicing these techniques together will reinforce the benefit and improve the outcome of the training.
What your employees need to do when handling patients
As referenced earlier in the article, the best practice is to avoid manual lifting and instead use assistive devices such as the mechanical lift when possible. Train your employees on how to use assistive devices and review the manufacturer’s instructions.
If mechanical lifts are not available, team lifting is the next safest option. Two people working together, to lift and move a patient, help reduce the forces required to lift the patient. Don’t hesitate to ask for help. Good communication with each other and the patient make lifting and transfers smooth and safe. Patients who are afraid and/or in pain will cooperate more if they understand the plan and know what to expect.
To assist in standing or transfers, bring the weight of the patient forward in the chair. This initiates the patient’s muscles and allows them to assist with the transfer process—which can also help reduce stress on the worker. Because the center of mass in the human body is generally located right at the waist, behind the belly button, it is the most difficult or heaviest part of the body to lift when helping someone to stand up. Assisting the patient to bend forward, bringing their nose over their toes, will get their hips off the chair or bed and make it easier for them to stand or pivot.
If a patient has a one-sided weakness, always transfer towards the stronger side of the patient. When assisting a patient from the bed to a wheelchair, this means placing the wheelchair on the stronger side of the patient. The patient will then be able to assist by using their stronger leg. Remember to switch the position of the wheelchair when helping the patient back to bed so they are still helping with their stronger side. Working from the patient’s stronger side also applies when helping someone stand. Assist the patient on their weaker side as they walk.
Lay patient flat, by lowering the bed, before assisting them in sliding up towards the head of the bed. Laying the bed flat reduces the forces required to assist a patient up towards their pillow. Ask the patient to assist you, if able, by pushing with their feet. This procedure is easier with two people.
Get close to the patient when helping them roll onto their side. For patient care or for the comfort of the patient, it may be necessary to position the patient onto their side. The healthcare worker needs to get as close to the patient as possible, and use the sheet near their hips to assist as needed. When guardrails are present, for patient safety, it is better for employees to push rather than pull. Bending the patient’s top leg allows some leverage to help get the patients hips over to the side as well. Remember to ask for help if a coworker is available to assist.
What to cover at your safety meeting on patient handling
Make sure your workers know how to perform these tasks and are comfortable working with the equipment available to them to help move patients. These steps and tools are designed to protect your workers and their patients. Among the topics to cover:
- How assistive devices such as the mechanical lift work
- The next best way to move a patient if a mechanical lift is not available
- Why assisting a patient to bend forward at the hips helps reduce the forces required for lifting
- How to prepare equipment, like the chair or wheelchair, before moving a patient with one-sided weakness
- Why you should lay a patient flat before assisting them to slide up in the bed
- When rolling a patient on their side, know what position you should be in and how to position a patient
According to OSHA, in 2017 nursing assistants had the second highest number of cases of musculoskeletal disorders. These injuries are due, in a large part, to overexertion related to manual patient handling activities. Due to the influx of patients, overworked and understaffed hospitals and medical care centers, this industry tops the list of workplace injuries. It is more important than ever, as the employer, to provide the right equipment and proper training in this physically demanding line of work.